What is the standard for vibrating screens in coal mines?
Vibrating screens used in coal mines are crucial for the efficient separation and sizing of coal and other minerals. Standards for these screens ensure their performance, safety, and reliability in harsh mining environments. Various standards and guidelines apply depending on the region and specific application. Here are key standards and considerations for vibrating screens in coal mines.
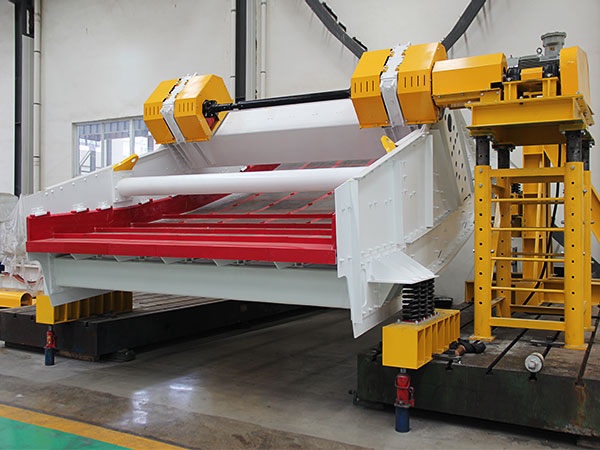
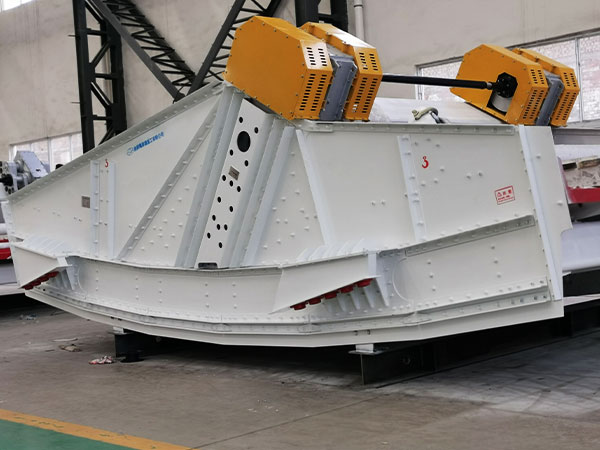
Vibrating screen standard for coal mines

Key Standards and Guidelines
ISO 17827 (International Standard):
- Description: Provides guidelines for the determination of the particle size distribution of coal by sieving.
- Application: Relevant for the design and testing of vibrating screens used for coal sizing.
ISO 9001 (Quality Management):
- Description: A general standard for quality management systems, applicable to manufacturers of vibrating screens.
- Application: Ensures that the design and production processes meet quality standards, leading to reliable and effective screening equipment.
ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers):
- Description: Provides various codes and standards related to mechanical equipment, including those that might apply to vibrating screens.
- Application: Ensures that the construction and operation of vibrating screens meet safety and performance requirements.
AIME (American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical, and Petroleum Engineers) Standards:
- Description: Includes guidelines specific to mining equipment, which may cover aspects related to vibrating screens.
- Application: Ensures that equipment used in mining operations, including vibrating screens, is suitable for the demanding conditions.
API (American Petroleum Institute):
- Description: Provides standards for equipment used in the petroleum and natural gas industries, which may include screening equipment.
- Application: Ensures that the vibrating screens meet performance and safety standards in related applications.
Design Considerations

Screen Material and Construction:
Material: Vibrating screens are typically constructed from high-strength steel or other durable materials to withstand the abrasive nature of coal and other mined materials.
Construction: Must be robust and designed to handle high loads and vibrations. This includes the use of reinforced frames and heavy-duty springs.
Screen Size and Capacity:
Size: Screens are available in various sizes and configurations to suit different throughput requirements and space constraints.
Capacity: The design must accommodate the volume of material to be processed without compromising performance.
Screen Type and Motion:
Type: Different types of vibrating screens include linear, circular, and elliptical motion screens. The choice depends on the specific application and material characteristics.
Motion: The motion of the screen affects the separation efficiency and capacity. Design parameters should be optimized for the material being screened.
Safety Features:
Guarding: Adequate guarding should be provided to prevent accidental contact with moving parts.
Emergency Stops: Emergency stop systems should be in place to allow for immediate cessation of operation in case of a malfunction or safety issue.
Maintenance and Accessibility:
Maintenance Access: Screens should be designed for easy access to components for maintenance and repairs.
Serviceability: Replaceable parts and easy-to-service components help minimize downtime.
Noise and Vibration Control:
Noise: Measures should be taken to control noise levels generated by the vibrating screen, as excessive noise can be a concern in mining operations.
Vibration: Proper balancing and isolation techniques should be employed to minimize the impact of vibrations on surrounding equipment and structures.
Compliance and Certification

Local Regulations: Ensure compliance with local regulations and industry standards specific to the region where the vibrating screens will be used.
Certifications: Look for equipment that meets relevant certifications or approvals for use in mining operations.
By adhering to these standards and considerations, vibrating screens can be optimized for performance, safety, and durability in coal mining operations. Always consult with equipment manufacturers and industry experts to ensure that the chosen equipment meets all necessary requirements.